Bladder Wrack
Bladder Wrack is an algae that grows in bothaquatic freshwater. It can grow up to a height of 3 feet and salt water. Often referred to as blue-green algae, It is ausually familyfound ofon algaethe that are photosynthetic in nature.
It is onecoasts of the mostAtlantic popularocean, foodPacific supplementsocean, Baltic sea, and tastein enhancerssome parts of Canada. These seaweeds are yellowish brown in color and have air-like sacs or bladders on the surface of the leaf.
This seaweed has been used byfor chefscenturies allin aroundtreatment thefor world.iodine Itdeficiency, comesweight-loss, packedjoint withpain, nutritionskin-related resultingailments, digestive and urinary problems.
Bladder Wrack has a numbersalty offish healthtaste. benefits.
Spirulina is super rich in proteins - about 60% to 70% of spirulina is made up to proteins. In addition, itIt is rich in minerals likeIodine, Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, Potassium, Sodium, Phosphorus,and Copper,other Manganese,essential Zinc, Cobalt, Sulfurminerals and Chromium.compounds.
Spirulina is a good source for vitamins like β-carotene (Pro-vitamin A), Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B6, Vitamin E, Vitamin K, Niacin, Pantothenic acid, Biotin, and Folic acid.
Its other ingredients include dietary fibers, polysaccharides, Linoleic acid, Zeaxanthin, Chlorophyll a, and Nucleic acids that help in the general well being of humans.
Cultivating and Harvesting SpirulinaHarvesting
SpirulinaBladder Wrack needs sea water sunlight, nutrients and carbonsunlight. dioxideLarge scale and commercial cultivation of this seaweed is being researched. However Bladder Wrack naturally grows in abundance along the coastlines.
Harvesters generally harvest them from their natural habitat. The best time to harvest is at low tide. Harvesters wade into the shallow waters and cut the sea weed.
Harvesting is done using using scissors or garden clippers. Pulling of the seaweed from the base is not recommended. Harvesters cut off only about half the size of the seaweed. This allows Bladder Wrack to grow andback.
Usually, colonies. It can be in small tanks or containers placed onafter a rooftopbig orstorm, inpiles large cultivation tanks in a farm. Spirulina grows naturally in sea water,of fresh water,seaweed are washed ashore. Harvesters collect these and greyuse waterthem asfor well. food and medicine.
Requirements
The following are required to cultivate and harvest spirulina.
Spirulina cultureContainerWaterNutrients
Spirulina Culture
Spirulina can be carefully extracted from rocks, walls or stones or are available commercially from botanical or marine stores.
Container
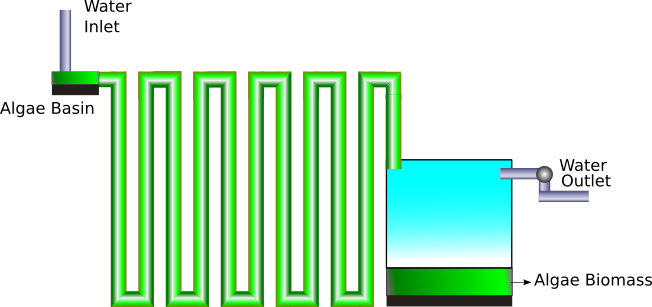
Plastic containers or aquariums can be used to cultivate algae. Spirulina needs sunlight so a transparent container is a good way to increase exposure to sunlight. Commercially spirulina is also grown in transparent vertical pipes or horizontal cultivation trays. The following illustration shows a schematic diagram that can be placed vertically or horizontally for large-scale cultivation.
Figure 1 - Schematic diagram of an algae farm
If cultivating in open tanks or trays, a greenhouse protection is needed to protect spirulina from rains, dust and insects.
Water
Spirulina grows in Sea water and fresh. When cultivating on land-farms, chlorine-free water is the most effective medium to grow spirulina.
Note: Spirulina can grow in grey water as well. Grey water is the waste water from kitchens, showers and laundry machines. Spirulina cultivated in grey water is will need further steps of purification before consuming. It is not recommended unless cultivated in areas where there there is a shortage of water.
Nutrients
Spirulina culture nutrients are commercially available at local agricultural or botanical stores or can be ordered online. Ensure that the nutrients contain the following compounds:
Sodium bicarbonateMagnesium sulfatePotassium nitrateCitric acidSaltUreaCalcium chlorideIron sulfateAmmonium sulfate
Cultivating Spirulina
Spirulina can be cultivated with as much as a test tube of fresh live algae. Place the spirulina in the algae basin and add nutrients at regular intervals of time. Within 5 to 6 weeks, in the right protected conditions, spirulina grows to form an algae biomass.
Harvesting Spirulina
After 5 to 6 weeks, the spirulina biomass is removed from the tray and filtered using a soft cloth. Filtration removes the water and spirulina is now available as a dark-green, slimy, sticky semi-fluid matter.
Consuming and Storing Spirulina
Bladder Wrack
AtBladder this stage, spirulina is at its nutritional best. It is freshly harvested and packed with nutrients, andWrack can be consumedeaten immediately. raw Itor is odorless and tasteless, and can be mixed with other foods and beverages for its umami flavor.
Spirulina can also be stored in closed containers and refrigerated.cooked. It has a shelfsalty-fish lifeline ofumami 2 weeks. taste. It canis also bedried, driedpowdered and processedstored. intoIn powders,some pillstraditions, it is brewed as tea, and tabletsis forcalled longBladder termWrack use.tea.